市場価格予測におけるバックテストについてはPythonのツールも多く出ており、本ブログでも何回か取り上げています。今回はvectorbtライブラリに関してです。いつも通り、Medium英文記事をベースとしています。vectorbtライブラリはベクトル並列計算などを用いて高速でバックテストやパラメータのチューニングが行えるライブラリです。ごく最近リリースされたものではありませんが、ネット上でのチュートリアルや解説記事はあまり多くありません。実用という所とは少し外れているからかもしれませんが、試してみる価値はあります。使い方もかなり込み入っています。本ブログでも原記事のコードをほぼ踏襲しています。
まず、必要なライブラリをインポートします。
import numpy as np import pandas as pd import yfinance as yf import vectorbt as vbt import seaborn as sns import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from datetime import date, datetime, timedelta import warnings warnings.simplefilter(action="ignore", category=FutureWarning)
原記事では、シグナル判定にChande Momentum Oscillator (CMO)とTrix Indicatorを用いていますが、以下はそれらの指標の計算関数です。
# Chande Momentum Oscillator (CMO) def chande_momentum_oscillator(df, period=14): df['CMO'] = ((df['Close'] - df['Close'].shift(period)).rolling(window=period).sum()) / \ ((df['Close'] - df['Close'].shift(1)).abs().rolling(window=period).sum()) * 100 return df['CMO'] # Trix Indicator def trix(df, period=14): df['Trix'] = df['Close'].ewm(span=period, min_periods=period).mean() df['Trix_Signal'] = df['Trix'].ewm(span=period, min_periods=period).mean() return df['Trix'], df['Trix_Signal']
次に、株価データを読み込みます。
ticker = '9432.T' end_date = datetime.today() start_date = end_date - timedelta(days=730) df = yf.download(ticker, start_date, end_date) df.columns = [col[0] if isinstance(col, tuple) else col for col in df.columns]
次に、指標のパラメータを引数として、トータルリターンを返り値とする関数を定義します。ここで参入と退出の戦略を定め、vectorbtライブラリでポートフォリオを計算しています。
# Function to calculate portfolio performance def calculate_performance(cmo_period, trix_period): # Calculate CMO and Trix for each period df['CMO'] = chande_momentum_oscillator(df, cmo_period) df['Trix'], df['Trix_Signal'] = trix(df, trix_period) # Define entry and exit signals based on CMO and Trix df['Entry'] = ( (df['CMO'] > 0) & # CMO crosses above 0 (df['Trix'] > df['Trix_Signal']) # Trix crosses above Trix Signal line ) df['Exit'] = ( (df['CMO'] < 0) & # CMO crosses below 0 (df['Trix'] < df['Trix_Signal']) # Trix crosses below Trix Signal line ) # Filter data for test only df_filtered = df[(df.index.year >= 2020) & (df.index.year <= 2025)] # Convert signals to boolean arrays entries = df_filtered['Entry'].to_numpy() exits = df_filtered['Exit'].to_numpy() # Backtest using vectorbt portfolio = vbt.Portfolio.from_signals( close=df_filtered['Close'], entries=entries, exits=exits, init_cash=100_000, fees=0.001 ) # Return total return as performance metric return portfolio.total_return()
次に、指定された範囲でパラメータ値を動かしてリターン最大のポイントを探索しています。
# Define the range of periods for optimization cmo_period_range = range(1, 21) # Example range for CMO period trix_period_range = range(1, 21) # Example range for Trix period # Create an empty matrix to store the total returns for each combination of periods total_returns_matrix = np.zeros((len(cmo_period_range), len(trix_period_range))) # Loop over all combinations of periods and store the total returns for i, cmo_period in enumerate(cmo_period_range): for j, trix_period in enumerate(trix_period_range): total_returns_matrix[i, j] = calculate_performance(cmo_period, trix_period) # Find the best parameters based on the highest total return best_cmo_period_idx, best_trix_period_idx = np.unravel_index(np.argmax(total_returns_matrix), total_returns_matrix.shape) best_cmo_period = cmo_period_range[best_cmo_period_idx] best_trix_period = trix_period_range[best_trix_period_idx] print(f"Best CMO Period: {best_cmo_period}") print(f"Best Trix Period: {best_trix_period}") print(f"Best Total Return: {total_returns_matrix[best_cmo_period_idx, best_trix_period_idx]}")

そして、パラメータ探索のヒートマップを図示します。最も色の濃い場所が最適解です。
# Plot the heatmap of total returns plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8)) sns.heatmap(total_returns_matrix, annot=False, cmap="YlGnBu", xticklabels=trix_period_range, yticklabels=cmo_period_range) plt.title('Heatmap of Total Returns for CMO and Trix Periods') plt.xlabel('Trix Period') plt.ylabel('CMO Period') plt.show()

次に、最適化されたパラメータ値を用いてバックテストを行っています。
# Now, calculate the portfolio using the best parameters df['CMO'] = chande_momentum_oscillator(df, best_cmo_period) df['Trix'], df['Trix_Signal'] = trix(df, best_trix_period) # Define entry and exit signals df['Entry'] = ( (df['CMO'] > 0) & (df['Trix'] > df['Trix_Signal']) ) df['Exit'] = ( (df['CMO'] < 0) & (df['Trix'] < df['Trix_Signal']) ) # Filter data for test only df_filtered = df[(df.index.year >= 2020) & (df.index.year <= 2025)] # Convert signals to boolean arrays entries = df_filtered['Entry'].to_numpy() exits = df_filtered['Exit'].to_numpy() # Backtest using vectorbt portfolio = vbt.Portfolio.from_signals( close=df_filtered['Close'], entries=entries, exits=exits, init_cash=100_000, fees=0.001, freq='d' ) # Display performance metrics and plot print(portfolio.stats(group_by=True)) portfolio.plot().show()
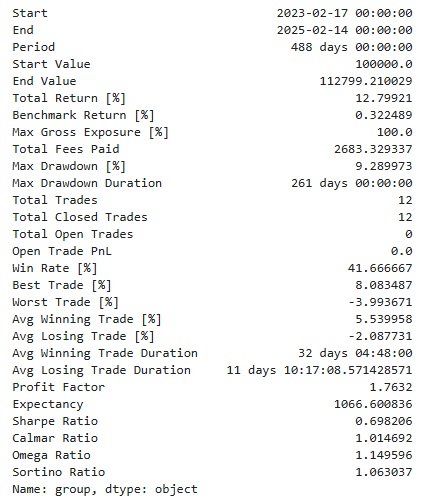
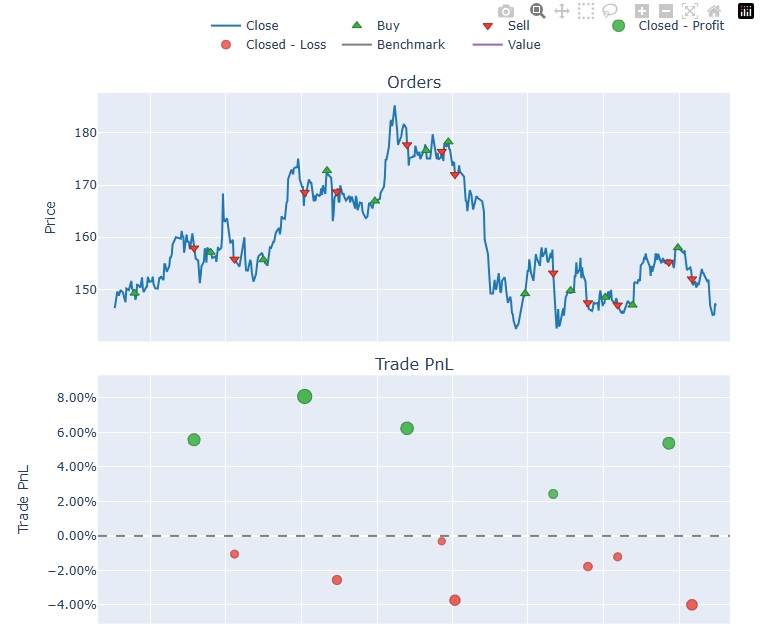

このように簡単なコマンドでバックテスト結果を図示することができます。